Since childhood, I’ve marveled at the crackling flames of a cozy fire, mesmerized by the warmth it exuded. With each log added, I couldn’t help but ponder: is the burning of wood an exothermic or endothermic process? To quench my curiosity, I embarked on a quest for a comprehensive understanding of this captivating phenomenon.

Image: online-learning-college.com
Exothermic Processes: A Release of Energy
In the realm of chemistry, exothermic processes are reactions that release energy into their surroundings. This released energy often manifests as heat, light, or sound. For instance, the combustion of wood, widely used as a fuel source, is a classic example of an exothermic process.
The Chemistry Behind Wood’s Exothermic Combustion
When wood burns, a complex set of chemical reactions unfolds. The primary reaction involves the combination of wood’s major components—cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin—with oxygen from the air. The heat generated during this reaction originates from the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. As the wood’s molecular structure is rearranged, energy is released in the form of heat.
Stages of Wood Combustion
- Ignition: Wood must reach a temperature of approximately 280°C for combustion to initiate.
- Smoldering: Incomplete combustion occurs, producing smoke, carbon monoxide, and small flames.
- Flaming Combustion: Abundant oxygen fosters complete combustion, resulting in blazing flames and maximum heat output.
- Ember Formation: Remaining carbon glows as embers, continuing to release heat albeit at a reduced rate.
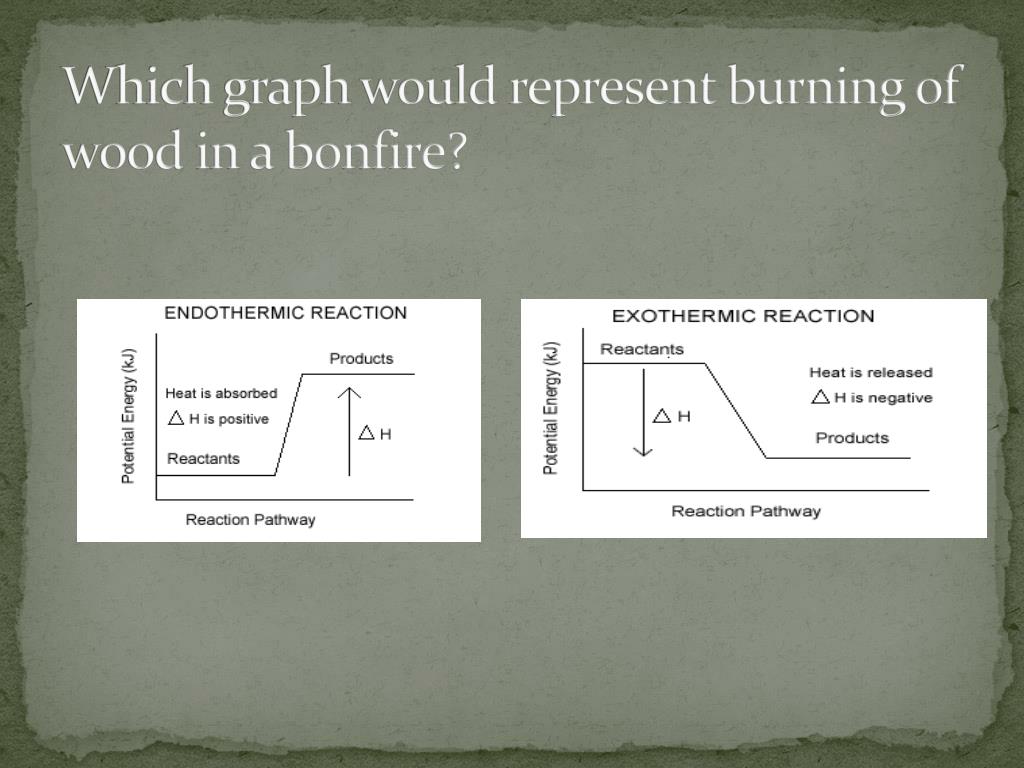
Image: www.slideserve.com
Variables Affecting Combustion Efficiency
The efficiency of wood combustion hinges on several factors, including:
- Wood Type: Different wood species exhibit varying heating values, influencing the amount of heat released.
- Moisture Content: Wetter wood requires more energy to evaporate moisture, reducing heat output.
- Airflow: Sufficient oxygen supply is essential for complete combustion and maximizing heat release.
- Stove/Fireplace Design: Efficient appliances channel heat effectively, reducing heat loss.
Latest Trends and Developments: Smart Burners
In the pursuit of optimizing wood burning efficiency, smart burners have emerged as a cutting-edge solution. These devices harness advanced sensors and automated controls to continuously monitor and adjust oxygen levels based on real-time conditions. By accurately controlling combustion, smart burners enhance heat output, reduce harmful emissions, and extend the lifespan of heating appliances.
Tips for Efficient and Safe Wood Burning
As an experienced blogger, I’ve compiled a set of practical tips to help you maximize your wood-burning experience:
Expert Advice for Optimal Performance
- Season Your Wood: Air-drying wood for at least six months reduces moisture content, improving combustion efficiency.
- Start Fires Properly: Use kindling and a chimney starter for a swift and controlled flame.
- Maintain Proper Airflow: Ensure adequate ventilation by opening vents or dampers to allow oxygen to enter.
- Burn Hot and Clean: Keep fires blazing brightly to promote complete combustion and minimize smoke.
- Clean Your Stove/Fireplace Regularly: Removing ash and soot buildup improves airflow and enhances efficiency.
FAQ: Common Wood Burning Queries Answered
Q: Why does my wood burn slowly?
A: Moist wood, insufficient airflow, or improper stove operation can hinder combustion.
Q: What is the best wood for heating?
A: Hardwoods like oak, maple, and birch offer high heating values and emit less smoke.
Q: How can I minimize creosote buildup?
A: Burn dry, seasoned wood at high temperatures and use a chimney liner.
Q: Is wood burning harmful to the environment?
A: Harvesting practices, stove efficiency, and wood source contribute to the environmental impact of wood burning.
Burning Of Wood Is Exothermic Or Endothermic
Conclusion: Unveiling the Heat’s Source
Through our exploration, we’ve uncovered the exothermic nature of wood burning, unraveling the intricate chemistry that unlocks its warmth. By comprehending the dynamics of combustion, we gain the knowledge to burn wood efficiently and safely, harnessing this renewable resource for our comfort while considering its environmental implications.
Whether you gather around a crackling fire for solace or rely on wood for heating your home, the understanding gained from this article will enrich your experiences with this enchanting, energy-releasing process. If you’re captivated by the theme of wood burning and its implications, I encourage you to delve deeper into the subject—who knows what fascinating revelations await you?