When two or more chemical substances come into contact, they engage in a reaction that results in the creation of new substances with distinct qualities. Understanding the products created in these reactions is crucial in various scientific disciplines, including chemistry, biochemistry, and material science. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of chemical reactions and embark on a journey to predict the products of a specific reaction, exploring the factors that govern the outcome and analyzing the implications of our findings.
Image: www.coursehero.com
Factors Influencing Reaction Products
Chemical reactions are guided by a set of fundamental principles that determine the identity of the products formed. These factors include:
-
Reactant Properties: The nature of the reacting substances, such as their molecular structure, functional groups, and reactivity, significantly influences the reaction outcome.
-
Reaction Conditions: Temperature, pressure, and the presence of catalysts or inhibitors can alter the reaction pathway and affect product formation.
-
Stoichiometry: The relative proportions of reactants dictate the limiting reagent, which determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed.
-
Reaction Mechanism: The sequence of elementary steps through which the reaction proceeds influences the intermediates formed and the final product distribution.
Predicting Reaction Products
Predicting the products of a chemical reaction involves applying our knowledge of these governing factors. Here are some key strategies used by chemists:
-
Balancing Chemical Equations: Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element remains the same on both sides of the equation. This allows us to determine the stoichiometric ratios of reactants and products.
-
Recognizing Functional Group Transformations: Understanding how functional groups react under specific conditions enables us to predict the changes that will occur during the reaction.
-
Applying Chemical Reactivity Rules: Established rules, such as Markovnikov’s rule and Zaitsev’s rule, guide the regio- and stereoselectivity of certain reactions, allowing us to anticipate the major product distribution.
A Case Study: Predicting the Products of a Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction
Nucleophilic substitution reactions are a common class of reactions involving the replacement of a leaving group by a nucleophile. Let’s take a closer look at a specific example to illustrate the process of product prediction:
-
Reaction: CH3Br + NaOH → ?
-
Prediction: Using our understanding of nucleophilic substitution reactions, we know that hydroxide ions (OH–) act as strong nucleophiles and bromide ions (Br–) are good leaving groups. Therefore, we can predict that the product of this reaction will be CH3OH (methanol) and NaBr (sodium bromide).
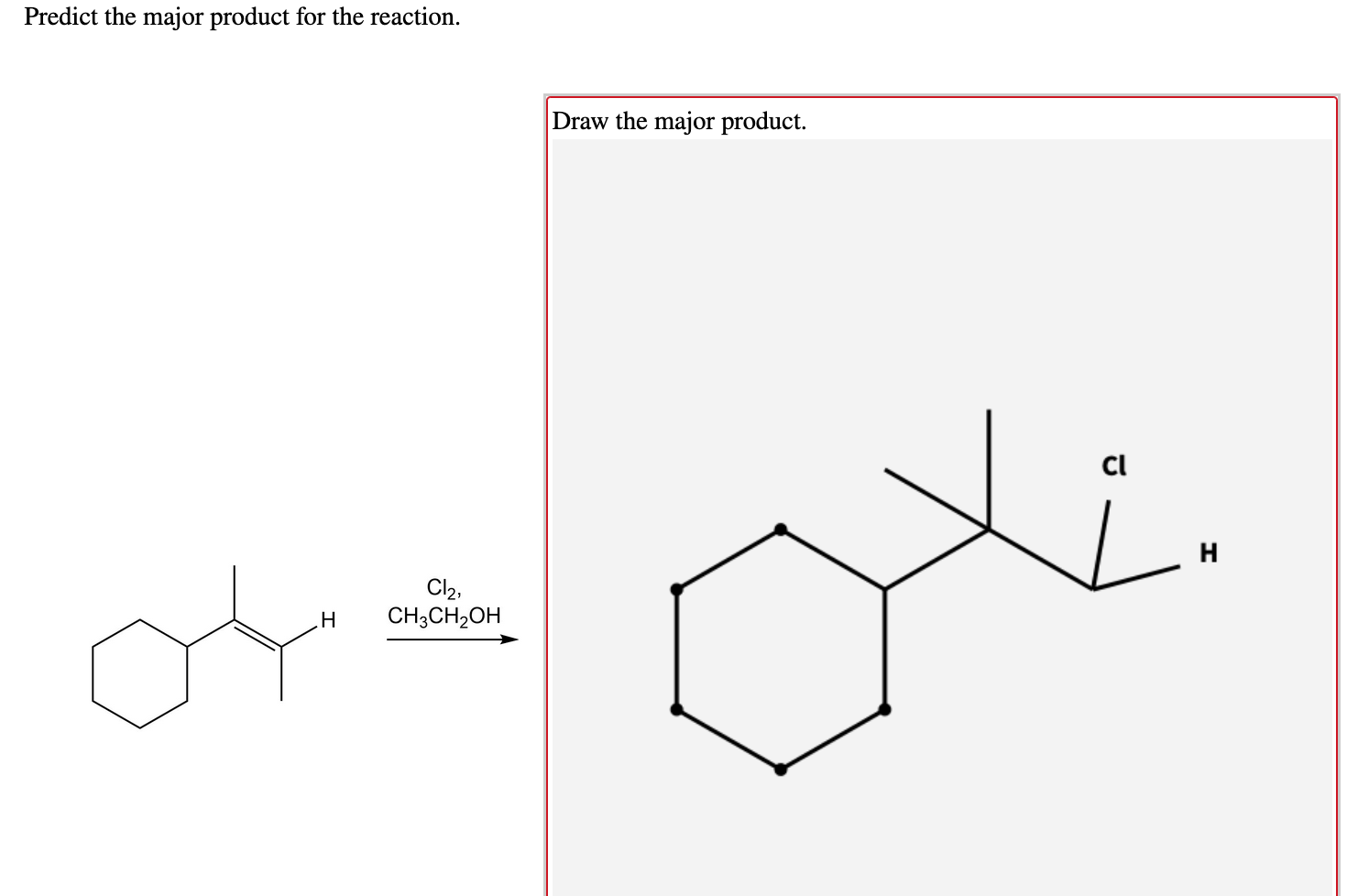
Image: www.chegg.com
Predict The Product S Of The Following Reaction
Conclusion
Predicting the products of a chemical reaction is a fundamental skill in various scientific disciplines. By understanding the factors that govern reaction outcomes and employing established strategies, we can make informed predictions about the identity and properties of the products. This ability plays a crucial role in designing and optimizing chemical processes, synthesizing new materials, and gaining insights into complex chemical transformations.